UMT - 长序列视频理解建模
- 标题:Unmasked Teacher: Towards Training-Efficient Video Foundation Models
- 时间:2023.3.28
- 作者团队:上海人工智能实验室
- 作者:Kunchang Li, Yali Wang, Yizhuo Li, Yi Wang, Yinan He, Limin Wang, Yu Qiao
- 有用指数:⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
- 贡献程度:⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
- 简单评价:在视觉编码器领域,主要有Knowledge distillation和mask modelling两个做法,这篇文章是较早提出这种方法的工作,给视频内容建模提供了一个比较好的思路。
- 一句话总结:作者还是试图用ViT + Q-former这两个在图像大模型领域常见的组合来建模视频,但为了更好建模视频的时序关系,用了masking的方式来抽取视频帧中的重要tokens作为ViT的输入,后续流程和传统的图像大模型instruction tuning差异不大。
Existing Gap
- 当前的视频建模方法还不完备,视频建模还处于探索期;
- 只通过抽帧的方式用图片大模型来完成对视频的建模,会对帧之间的时序关系理解不对,导致在一些视频任务上表现不佳。
- 难点在于,如何能建模视频,是模型能够在以下能力上有提升
- Duration:能input较长的视频长度;
- Appearance:能理解视频中的主体,能定位视频中某主体出现的时间;
- Motion:能理解主体的动作和变化的时序关系。
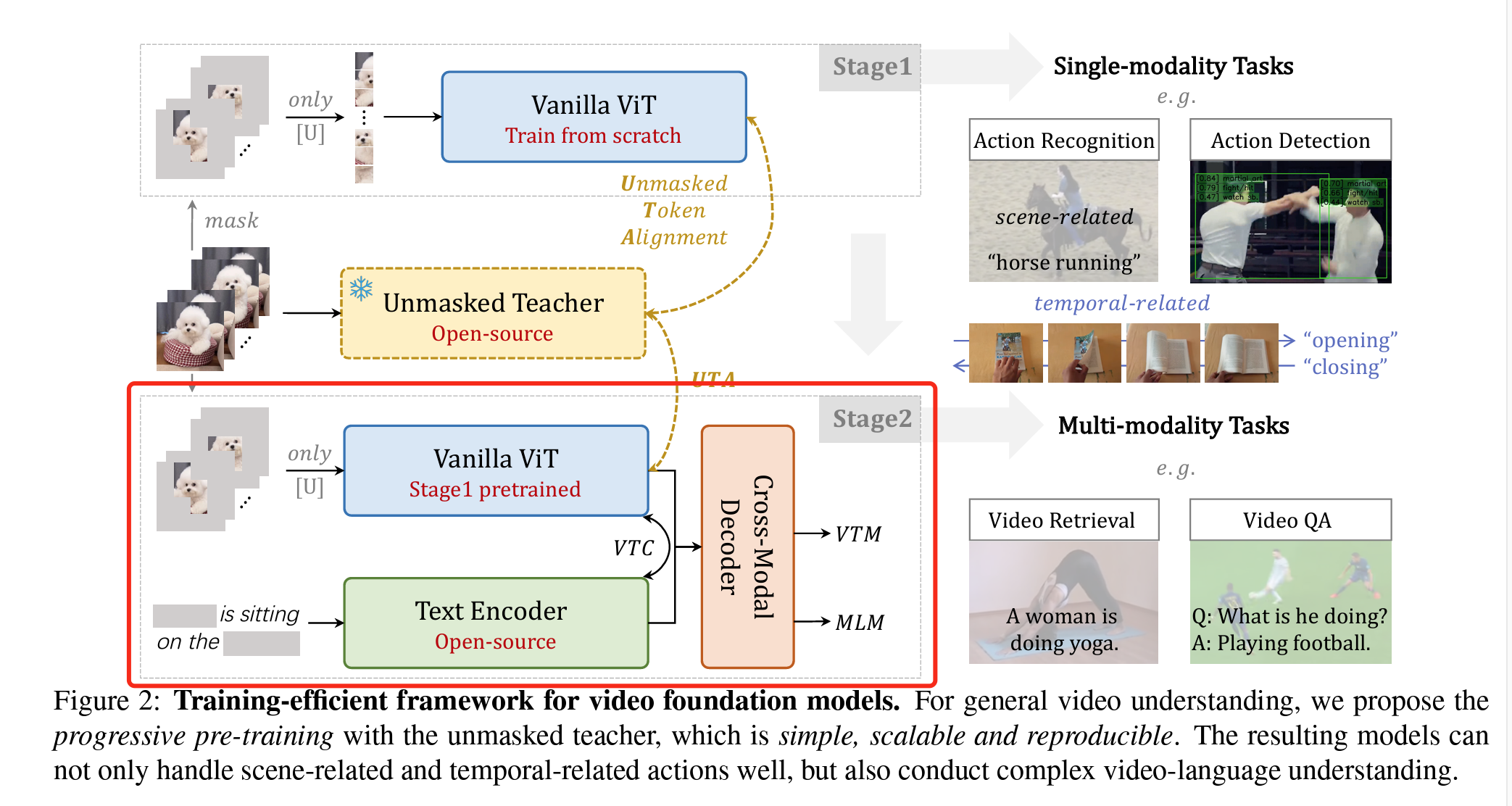
Proposed Solution
和图片大模型类似,作者的核心思想还是如何用到ViT的transformer架构来处理视频,但如果直接按照处理图片的思路,第一训练成本会大幅增加,其次视频之间相近帧之间的信息密度较小,冗余度较高。因此这里思考的一个思路可以是
如何只使用一些视频中更重要的内容进行训练?
作者提出使用两步进行建模
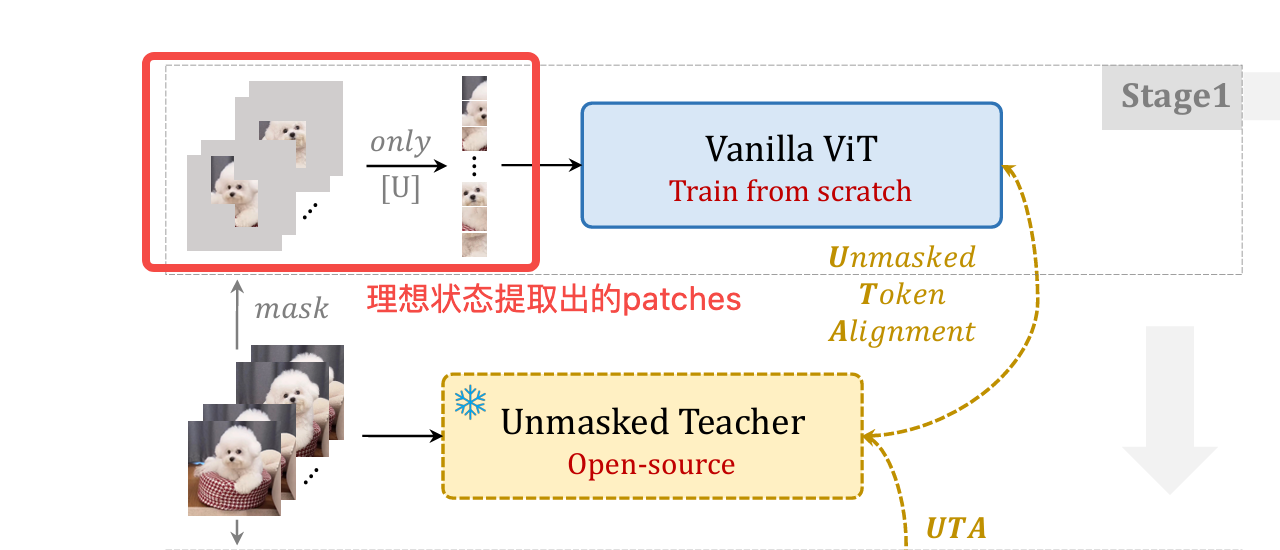
- Unmasked teacher
- 目标:降低训练成本条件下,对视频建模;
- 方法:mask掉视频抽帧80%的内容,只用剩下的20%作为ViT的patches,生成embedding,这20%的选择方法是,
- 第一,计算ViT模型的最后一层的attention score,对该score的multinomial distribution进行sample,得到这20%的patches。
- 第二,为了保证提取出语义上完整的patches,对该ViT模型进行了训练,即把masked过提取的patches加一层Linear projection,把维度对齐到没有masked的ViT提取的patches,和原ViT模型的结果求MSE loss,对原ViT模型进行训练,这样保证提取的patches语义上丢失的较少。因为这里是有一个teacher模型的,所以作者管这个训练叫做unmasked teacher,这个方法也叫做Knowledge distillation。
- 举例:红框中就是理想状态下提取的主体
- 训练数据:
- Pre-training
- 目标:把训练好的ViT模型和文本大模型进行对齐,这里和图片大模型的思路是完全一致的,只是用的Video<>text pair。
- 方法:这里和图片大模型的训练思路类似,这里使用了BLIP的架构,是Deep-fusion大类下的,其实就是用了Q-former进行深度的模态融合,保证文本模型能够理解ViT的输出,主要还是使用了类似bert的masked text prediction的loss,图文对比学习的loss,和图文匹配的loss。
Coding Explanation
主流程,UMT的forward函数
这里的Image的shape是[Batchsize, NumOfFrames, Channel, Height, Width]。
def forward(self, image, text, idx):
"""forward and calculate loss.
Args:
image (torch.Tensor): The input images. Shape: [B,T,C,H,W].
text (dict): TODO
idx (torch.Tensor): TODO
Returns: TODO
"""
self.clip_contrastive_temperature()
##
vision_embeds, pooled_vision_embeds, student_output, clip_output = self.encode_vision(image)
text_embeds, pooled_text_embeds = self.encode_text(text)
# obtain vision and text representations.
vision_proj = self.vision_proj(pooled_vision_embeds)
text_proj = self.text_proj(pooled_text_embeds)
# calculate loss
## MCA loss
if self.loss_weight.uta != 0:
loss_uta = self.criterion_uta.uta_loss(student_output, clip_output)
else:
loss_uta = torch.tensor(0)
## VTC loss
if self.loss_weight.vtc != 0:
loss_vtc = self.criterion_vtc_vtm.vtc_loss(
vision_proj, text_proj, idx, self.temp, all_gather=True
)
else:
loss_vtc = torch.tensor(0)
## VTM loss
if self.loss_weight.vtm != 0:
loss_vtm = self.criterion_vtc_vtm.vtm_loss(
self.get_text_encoder(),
self.itm_head,
self.temp,
vision_embeds,
text_embeds,
vision_proj,
text_proj,
text.attention_mask,
idx,
)
else:
loss_vtm = torch.tensor(0)
## MLM loss
if self.is_pretrain and self.loss_weight.mlm != 0:
loss_mlm = self.criterion_mlm.mlm_loss(
self.text_encoder, text, vision_embeds, None
)
else:
loss_mlm = torch.tensor(0)
return dict(
loss_uta=loss_uta * self.loss_weight.uta,
loss_vtc=loss_vtc * self.loss_weight.vtc,
loss_vtm=loss_vtm * self.loss_weight.vtm,
loss_mlm=loss_mlm * self.loss_weight.mlm,
)
第一阶段训练主要使用到UTA loss(unmasked token alignment loss),这个loss的主要计算逻辑,就是把正常CLIP输出的结果和要训练的student模型结果做一个MSE loss:
def uta_loss(self, student_output, clip_output):
"""forward to calculate the loss
Args:
student_output (torch.Tensor): The student output. Shape: [K,B,N,C].
clip_output (torch.Tensor): The teacher representation. Shape: [K,B,N,C].
Returns: loss_uta (torch.Tensor): The mask clip alignment loss. Shape: [].
"""
if self.norm_type == 'l2':
student_output = student_output / student_output.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
clip_output = clip_output / clip_output.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
elif self.norm_type == 'none':
pass
else:
raise NotImplementedError
if self.loss_type == 'l2':
loss_uta = (2 - 2 * (student_output * clip_output).sum(dim=-1)).mean()
elif self.loss_type in ['mse', 'smooth_l1']:
loss_uta = self.loss_func(input=student_output, target=clip_output)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
return loss_uta
这里的loss只用到了student output和CLIP output(未mask的output),这两个可以在image_encoder的代码中看到
https://github.com/OpenGVLab/unmasked_teacher/blob/4fb4049f5a87919882e68ccc427615ae7dab1c33/multi_modality/models/umt.py#L151
elif mask_type in 'attention':
clip_output, attn = self.clip_teacher(image)
BT, N = attn.shape
N_vis = N - int(N * mask_ratio)
importance = torch.multinomial(attn, N) # multinomial sampling选择attn score最高的tokens
mask = torch.ones((BT, N))
pos1 = torch.arange(BT).view(-1, 1).repeat(1, N_vis)
pos2 = importance[:, :N_vis]
mask[pos1, pos2] = 0
mask = mask.view(B, -1).to(torch.bool)
实验设置
两阶段训练数据设置
| 阶段 | 数据 | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| 阶段一 | Kinetics-710 | 60M video<>text pair |
| 阶段二 | COCO, SBU captions, WebVid | video text pairs |
Ablation实验设置
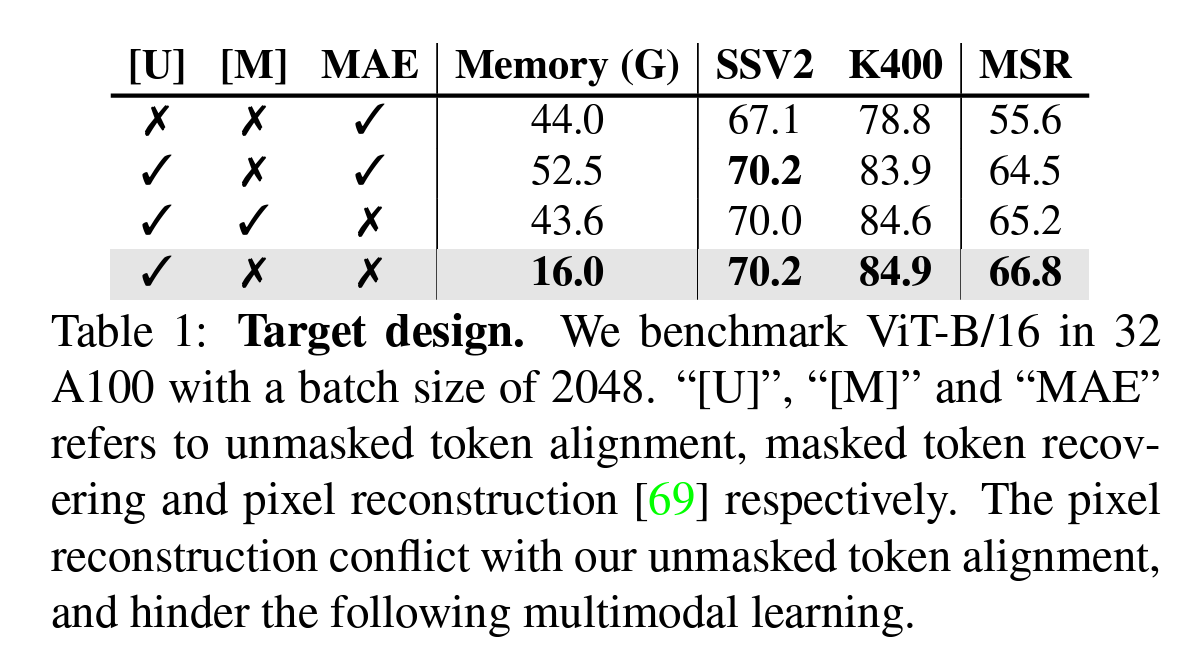
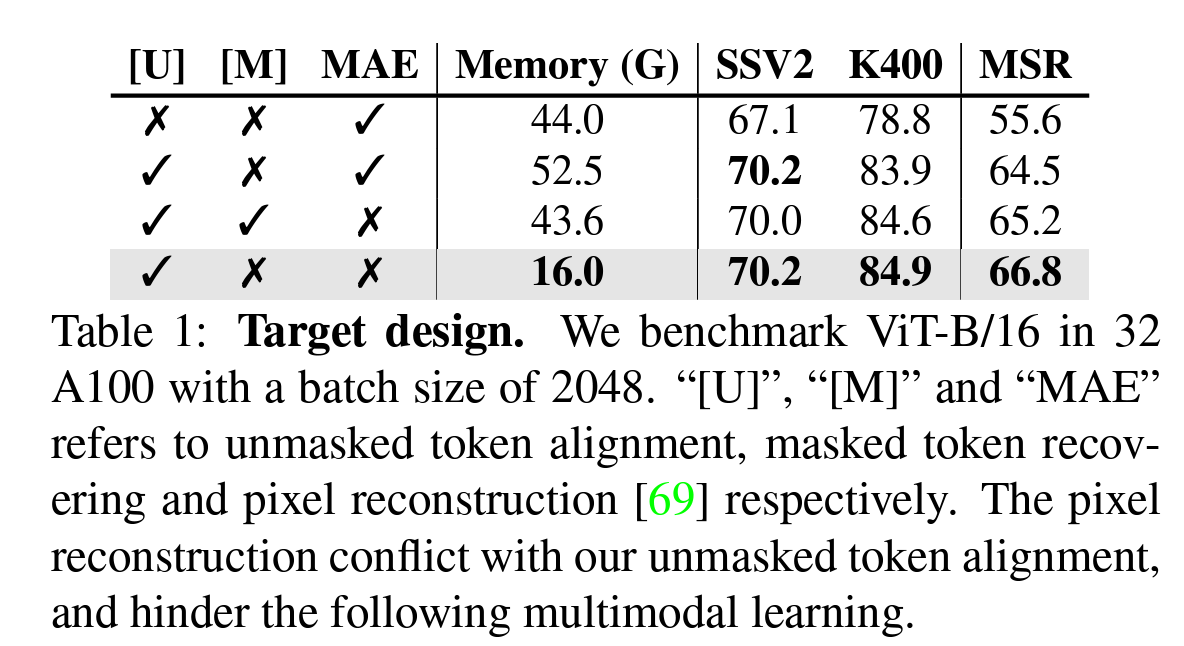
- 比较masked teacher和VideoMAE的pixel reconstruction方法的对比
- 比较不同mask type,Video frames sampling的区别
实验结果
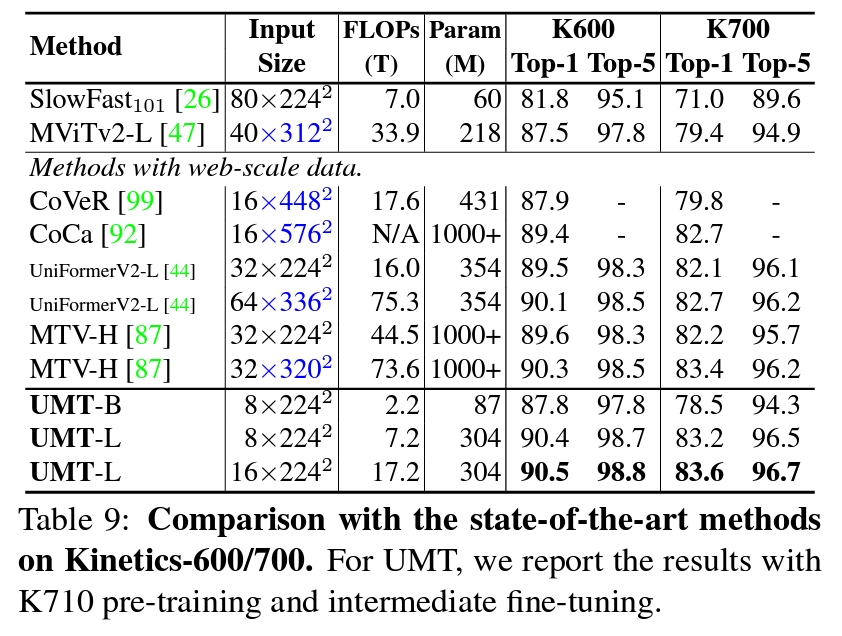
总结
UMT作为建模视频编码器的一个工作,是Knowledge distillation-based的方法,为后续相似的工作提供了一个不错的思路。在我看来,为了建模视频很多方法都会看上去很有用,他们的效率提升的核心就在于,如何能够能够对视频进行高效压缩,并且不丢失语义信息。
上篇AI算法