Reference
-
Key concepts
-
Policy Gradient
Key Concepts
What
定义
The agent’s policy $\pi(s)$ provides the guideline on what is the optimal action to take in a certain state with the goal to maximize the total rewards.
关键词,在某个state下,采取何种策略,能够让rewards的总和最大。
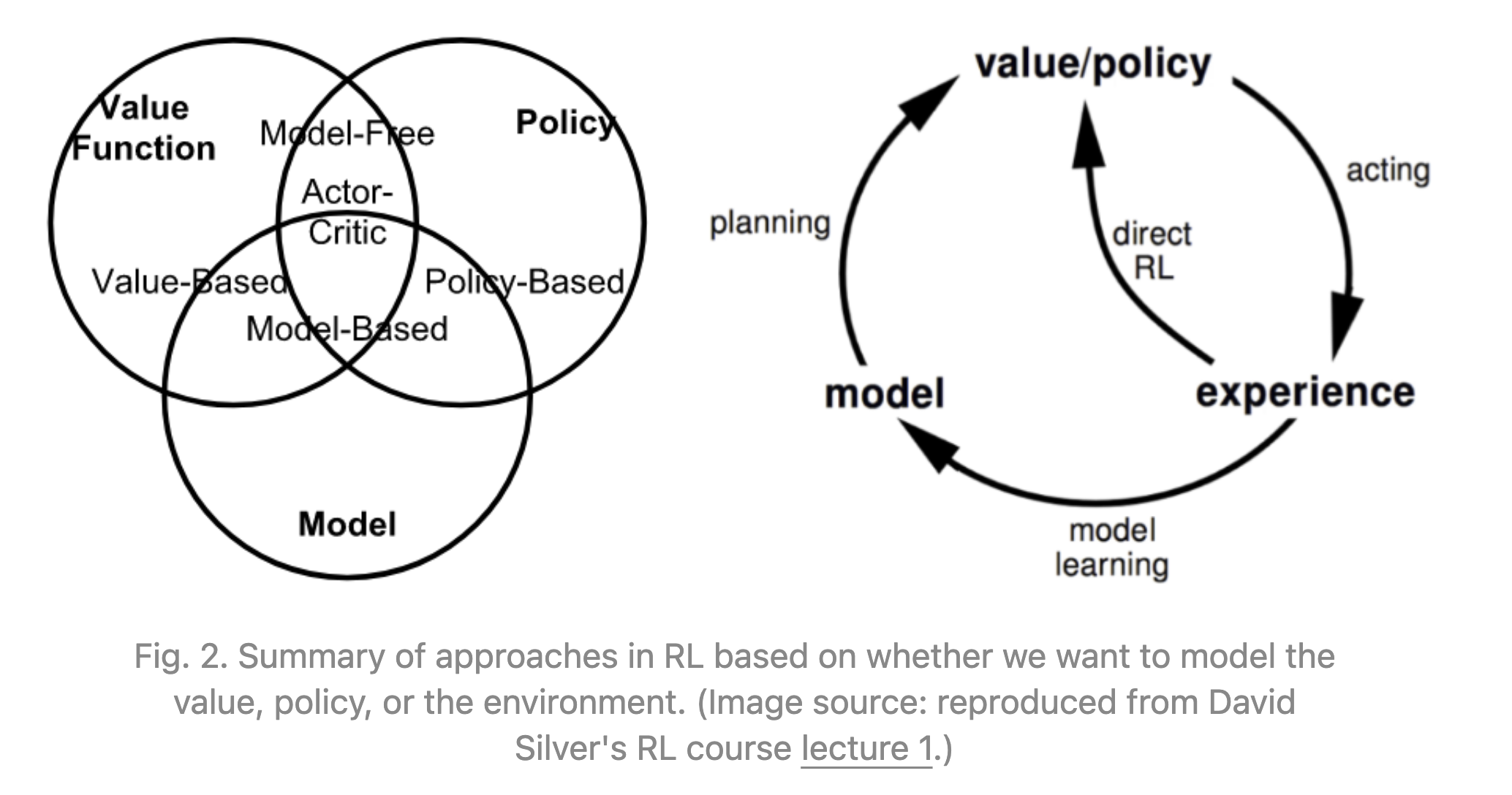
Model
模型就是对环境的一种描述,这种描述能够告诉参与者在当前状态下可采取的行动有哪些。主要由Transition probability function $P$ 和Reward function $R$ 组成。
Reward function $R$,预测被Action trigger后的下一次的Reward。
\[R(s, a)=\mathbb{E}\left[R_{t+1} \mid S_t=s, A_t=a\right]=\sum_{r \in \mathcal{R}} r \sum_{s^{\prime} \in \mathcal{S}} P\left(s^{\prime}, r \mid s, a\right)\]Transition Function $P$,定义在采取某个Action的情况下,State的变化规律。
\[P_{s s^{\prime}}^a=P\left(s^{\prime} \mid s, a\right)=\mathbb{P}\left[S_{t+1}=s^{\prime} \mid S_t=s, A_t=a\right]=\sum_{r \in \mathcal{R}} P\left(s^{\prime}, r \mid s, a\right)\]Policy
Policy就是行为描述函数,在某个状态 $s$ 下,需要采取何种策略。
- 确定性Policy:$\pi(s) = a$
- Stochastic Policy: $\pi(s) = \mathbb{P}[A = a \mid S = s]$
Value Function
通过对未来Reward的预测,来评价当前的state有多么rewarding。
\[G_t=R_{t+1}+\gamma R_{t+2}+\cdots=\sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \gamma^k R_{t+k+1}\]$\gamma$ 是打折系数,这个系数在0~1之间,因为
- 未来的Reward是预测的,且可能不准;
- 未来的Reward无法提供及时反馈;
- 未来Reward需要无限tracking。
State value: 在State s时,可以获得的return。 \(V_\pi(s)=\mathbb{E}_\pi\left[G_t \mid S_t=s\right]\)
Action Value:在某一个State下面采取某种Action所能得到的Value。也叫做Q-value \(Q_\pi(s, a)=\mathbb{E}_\pi\left[G_t \mid S_t=s, A_t=a\right]\)
除此之外,因为我们有某种策略$\pi$,因此我们可以通过策略和Action Value来计算得到State Value。
\[V_\pi(s)=\sum_{a \in \mathcal{A}} Q_\pi(s, a) \pi(a \mid s)\]还有一个定义叫做A-value,就是Advantage Value,是Action Value和State Value之间的差值,可以理解为采取某一个Action之后能比现在的State Value带来多少增益。
\[A_{\pi}(s, a) = Q_{\pi}(s, a) - V_{\pi}(s)\]Optimal Value & Policy
这就非常直白了,Optimal Value能够提供最大的Return,看公式$\eqref{op_v}$
\[V_*(s)=\max _\pi V_\pi(s), Q_*(s, a)=\max _\pi Q_\pi(s, a) \label{op_v}\]与此相对应的最优策略可以表达为
\[\pi_*=\arg \max _\pi V_\pi(s), \pi_*=\arg \max _\pi Q_\pi(s, a)\]这两者是否有冲突呢?
没有,因为最优策略就是Value function最大的时候的策略值。
Learning Type
- On-policy v.s. Off-policy: 核心区别在于学习时,如何更新Q-value。
- Off-Policy会在每个Action后采取最好的Action来更新$Q(s,a)$,
- 而On-Policy会用当前策略更新$Q(s,a)$。
- Policy-based v.s. Value-based:
- Value-based: 先学习Value function,再根据这个Value function来学习最优策略.
- Policy-based:显式学习一个Policy的representation,mapping $ \pi: s -> a$,这个mapping关系是存储在内存中的。
- Actor-critic:是以上两者的混合。
- 本质区别:Value指的是给定State $s_t$ 和动作$a_t$,可以获得累积奖励的期望值,因此这是一个更注重于未来收益最大化的衡量方式;Policy指的是,找到策略$\pi_t$,使得累积奖励的期望值最大化。
Markov Process
RL问题都可以看成一个Markov decision Process,MDP将问题简化为,所有未来的状态,都有且只与当前状态有关,历史状态都已经被encode到当前状态下了。
注意一下公式$\eqref{eq_bellman}$,如果我们想直接获得最优解而不是策略,我们其实不需要考虑策略$\pi$,而是直接根据状态转移矩阵计算Q-value和State Value。
\[\begin{aligned} V_*(s) & =\max _{a \in \mathcal{A}} Q_*(s, a) \\ Q_*(s, a) & =R(s, a)+\gamma \sum_{s^{\prime} \in \mathcal{S}} P_{s s^{\prime}}^a V_*\left(s^{\prime}\right) \\ V_*(s) & =\max _{a \in \mathcal{A}}\left(R(s, a)+\gamma \sum_{s^{\prime} \in \mathcal{S}} P_{s s^{\prime}}^a V_*\left(s^{\prime}\right)\right) \\ Q_*(s, a) & =R(s, a)+\gamma \sum_{s^{\prime} \in \mathcal{S}} P_{s s^{\prime}}^a \max _{a^{\prime} \in \mathcal{A}} Q_*\left(s^{\prime}, a^{\prime}\right) \end{aligned} \label{eq_bellman}\]Solutions
解决问题的目标:习得一个能够最大化未来Reward的Policy。
明确几个问题
- Episode和Action的区别:一个episode是一系列actions和states的组合,一个episode表示一个学习周期已经结束,达到了既定目标。一个Action仅表示一个动作。
Monte Carlo Method
- Reference:RL Lecture 5.pdf (umass.edu)
- 要解决的问题
- 在Model-free的场景下,习得一个episodic MDP模型的Value function的最大值 $V_{s_t}$ 和最优策略 $\pi_*(s)$ 。
- 根本思想是什么
- MC prediction: 根据state-Value function预测某个Policy在某个状态下的Value最大值。
- MC control:the task that is finding the optimal policy that maximize the value function by alternating between policy evaluation and policy improvements.
- 算法流程
- MC Evaluation
- MC control
- MC Evaluation
- 举例说明
21点游戏
- Objective: having your card sum greater than the dealers without exceeding 21.
- States
- current sum
- dealer’s showing card
- Do i have usable ace
- Reward
- +1 wining, 0 draw, -1 losing
- Actions
- Stick(stoping receiving cards),
- hit(receive another card)
- Policy
- Stick if sum is 20/21, else hit.
MC evaluation: 根据以上建模可以写一个MC Evaluation算法来确定这个Policy的Value是多少。
MC Control: 以上述Policy作为初始Policy,随后在某个states下,以$\epsilon$ 的概率选择更新为一个mean(reward)更大的策略,例如更新策略为在sum为16且有ace的情况下应该stick。
- 为什么该算法可以解决问题
通过MC Evaluation的迭代,计算每个episode的State Value function就能获得最大值。通过MC Control的迭代,在每个episode以一定概率选择Reward mean更高的Policy,可以获得最大Policy和最大的State Value。
- 优劣势
- 举例给人听
Policy Gradient
找到一个Policy gradient estimator并把这个estimator放到stochastic gradient ascent算法中进行迭代。
一个非常常见的estimator长这样。
\[\hat{g}=\hat{\mathbb{E}}_t\left[\nabla_\theta \log \pi_\theta\left(a_t \mid s_t\right) \hat{A}_t\right]\]计算gradient的时候直接对estimator求导。
- 为什么这个方法非常方便?
- 因为在代码里面,$\log \pi_\theta(a_t \mid s_t)$ 就是所有Token的log probabilities,大语言模型本质都是在预测下一个Token。在计算的时候,estimator的最优值可以直接通过求导得到。
- estimator有很多自动求解器,非常方便。
- 为什么这个方法有问题?
- 这个过程中有需要random sample,对sample之后的结果求导本身是无法解释的;
- 这种方法有可能导致Policy gradient非常大。
Monte Carlo Policy Gradient
算法流程
- Start with a random policy that tells you what action to take in a given situation.
- Try out this policy by interacting with the environment and see what reward you get at each time step.
- After each episode, look at the reward you got at each time step and calculate a return for each step. The return is the sum of all the rewards you received after that time step.
- Use these returns to update the policy. The update tells the policy to favor actions that got a higher return, by increasing the probability of taking these actions.
- Repeat steps 2-4 for multiple episodes until the policy gets better at the task.
- Use this improved policy to perform the intended task in the environment.
优势
- Policy-based能够直接优化Policy本身;
- 可以处理有随机Action的情况;
缺点
- Noisy Gradient
- High variance
Actor-Critic
Reference
| [Understanding Actor Critic Methods and A2C | by Chris Yoon | Towards Data Science](https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-actor-critic-methods-931b97b6df3f) |
- 要解决的问题是?
传统的Policy Gradient方法有很大的instability,且训练的时候很难收敛。因此要解决RL中以上的两个难题。
- 为什么可以解决问题?
TRPO
针对Policy gradient存在的问题,有人提出了Trust Region Method,简单来说就是加入了一个constraint,目的是为了防止某一次策略更新和上一次的策略收益偏差过大。但看公式本身$\eqref{eq_trpo}$其实和Policy gradient的差别并不大,只是加了一个上次策略作为分母。
\[\begin{array}{ll} \underset{\theta}{\operatorname{maximize}} & \hat{\mathbb{E}}_t\left[\frac{\pi_\theta\left(a_t \mid s_t\right)}{\pi_{\theta_{\text {old }}}\left(a_t \mid s_t\right)} \hat{A}_t\right] \\ \text { subject to } & \hat{\mathbb{E}}_t\left[\operatorname{KL}\left[\pi_{\theta_{\text {old }}}\left(\cdot \mid s_t\right), \pi_\theta\left(\cdot \mid s_t\right)\right]\right] \leq \delta . \end{array} \label{eq_trpo}\]在实际计算过程中,可以把使用surrogate Objective来代替这个constraint problem,比如下面这个Objective
\[\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{maximize}} \hat{\mathbb{E}}_t\left[\frac{\pi_\theta\left(a_t \mid s_t\right)}{\pi_{\theta_{\text {old }}}\left(a_t \mid s_t\right)} \hat{A}_t- \beta \mathrm{KL}\left[\pi_{\theta_{\text {old }}}\left(\cdot \mid s_t\right), \pi_\theta\left(\cdot \mid s_t\right)\right]\right]\]直接把constraint作为一个penalty。
最大的问题在于这个$\beta$ 并不好选,实际处理的时候在不同问题上$\beta$ 的选择非常影响结果。

