主要用来记录面试coding的代码技巧与解题思路。个人感觉总体来说面试代码很少会非常复杂,超过100行,一般来说100行以内都可以搞定,思路分析过程比题解更重要,如果没做出来的题可以分析一下,为什么没做出来。
Graphs/Trees
与树、图相关的算法主要就是几种遍历方法的熟练运用,其实很多题的内核都是可以依靠某种遍历方法来解。因此面对此类题的思考方法,我自己归纳为以下:
- 首先,对于二叉树,我需要的左右子树结果的顺序是什么?如果是左->根->右,那么中序遍历的写法,如果是左->右->根,那么是后序遍历的写法;
- 其次,每次遍历返回给我的结果需要什么,是一个全局最大值还是局部最优值?
- 最后我需要设置的递归结束的条件是什么?
示例
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
题目:
路径 被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,沿父节点-子节点连接,达到任意节点的序列。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 至多出现一次 。该路径 至少包含一个 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
路径和 是路径中各节点值的总和。
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其 最大路径和 。
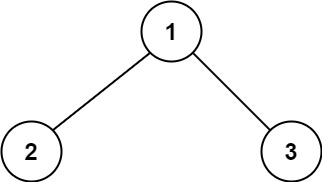
输入:root = [1,2,3]
输出:6
解释:最优路径是 2 -> 1 -> 3 ,路径和为 2 + 1 + 3 = 6
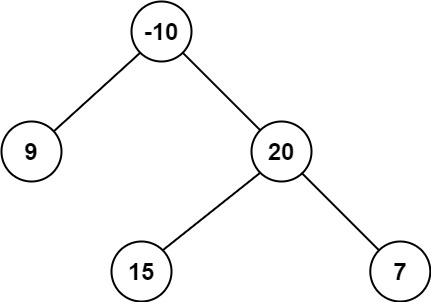
输入:root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:42
解释:最优路径是 15 -> 20 -> 7 ,路径和为 15 + 20 + 7 = 42
分析思路:
- 需要子树的最优结果,返回给根做更大值分析;
- 每次遍历返回的应该是一个子树的最大贡献值;
- 递归结束条件应该是空子树时返回。
我的错误解答:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maxPathSum(root *TreeNode) int {
var finalMax int
_ = helperMaxSum(root, &finalMax)
return finalMax
}
func helperMaxSum(root *TreeNode, currMax *int) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
left := helperMaxSum(root.Left, currMax)
right := helperMaxSum(root.Right, currMax)
maxOfCurrRoot := max(root.Val, max(root.Val + left, max(left, max(right, max(root.Val + left + right, root.Val + right)))))
if maxOfCurrRoot > *currMax {
*currMax = maxOfCurrRoot
}
return maxOfCurrRoot
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
我犯的错误是:
- 分析不够全面:如果一个子树包含在最终路径的解中,那么一定要包含根节点;
- 递归函数返回值错误:不应该返回子树的全局最大,而应该返回包含子树根节点的全局最大,因为如果需要用到该子树,那么一定要包含根节点,否则应该只更新全局最大值,而区分开子树的最大值跟递归函数的返回值。
根据我解答的改正:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func maxPathSum(root *TreeNode) int {
var finalMax int = -1 << 31
_ = helperMaxSum(root, &finalMax)
return finalMax
}
func helperMaxSum(root *TreeNode, currMax *int) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
left := max(helperMaxSum(root.Left, currMax), 0)
right := max(helperMaxSum(root.Right, currMax), 0)
maxOfCurrRoot := root.Val + left + right
*currMax = max(*currMax, maxOfCurrRoot)
return root.Val + max(left, right)
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
Graph的BFS与DFS遍历
Graph的BFS遍历使用queue的数据结构,DFS遍历使用stack的数据结构,两者的写法大概如下所示:
/**
* Definition for a graph node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* AdjList []*Node
* }
*/
// DFS search for graphs
// 1. Append root to stack
// 2. Start from the top elem from stack
// 3. Use a for loop to visit every elem in adj list
// 4. If an elem is not visited, put it in visited list, visit it
// 5. If an elem is visited, skip the operation
// 6. Pop the elem at the end of the loop
var visited map[*Node]bool{}
var startNode *Node
var stack []*Node{startNode}
for len(stack) != 0 {
top := stack[len(stack)-1]
if !visited[top] {
visited[top] = true
visit(top)
for _, adjNode := range top.AdjList {
stack = append(stack, adjNode)
}
}
stack = stack[:, len(stack)-1]
}
// BFS search for graphs
// 1. Append root to queue
// 2. Record the length l of current queue, which is all nodes in this level
// 3. Use a for loop to visit the first l elem in queue
// 4. If an elem is not visited, put it in visited list, visit it
// 5. If an elem is visited, skip the operation
// 6. Dequeue every elem after visited
var visited map[*Node]bool
var startNode *Node
var queue []*Node
for len(queue) != 0 {
l := len(queue)
for i:=0; i<l; i++ {
top := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if !visited[top] {
visited[top] = true
visit(top)
for _, adjNode := range top.AdjList {
queue = append(queue, adjNode)
}
}
}
}